mmSPLAM:
Millimeter-Wave Simultaneous Passive Mobile Target Tracking and Environment Reconstruction
Xinyuan Wei, Jian Wang
Motivation:
- WiFi sensing often treats the environment as interference, focusing on signal suppression.
- Most mmWave SLAM systems localize the transceiver itself, not passive or non-cooperative targets.
- Dedicated SLAM systems are expensive and complex.
Features:
- Passive millimeter-wave sensing without target cooperation.
- Joint mobile target tracking and environment reconstruction.
- No transmitter–receiver clock synchronization required.
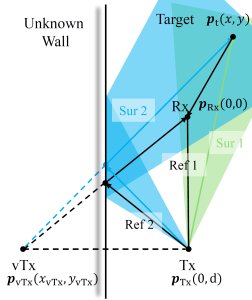

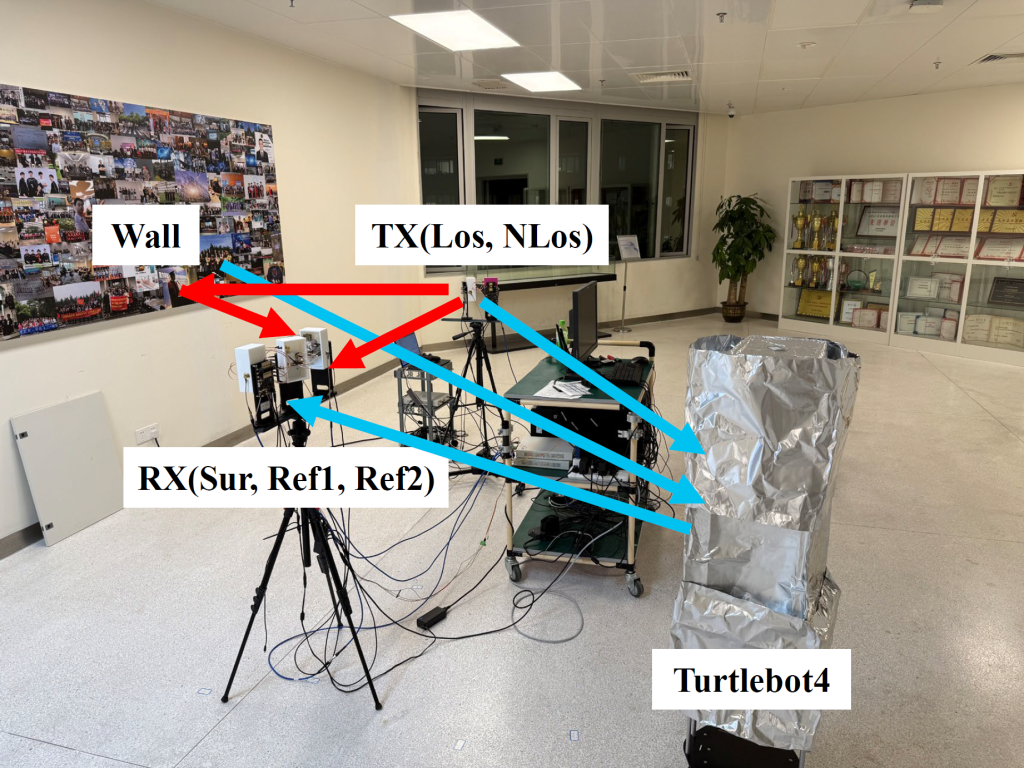
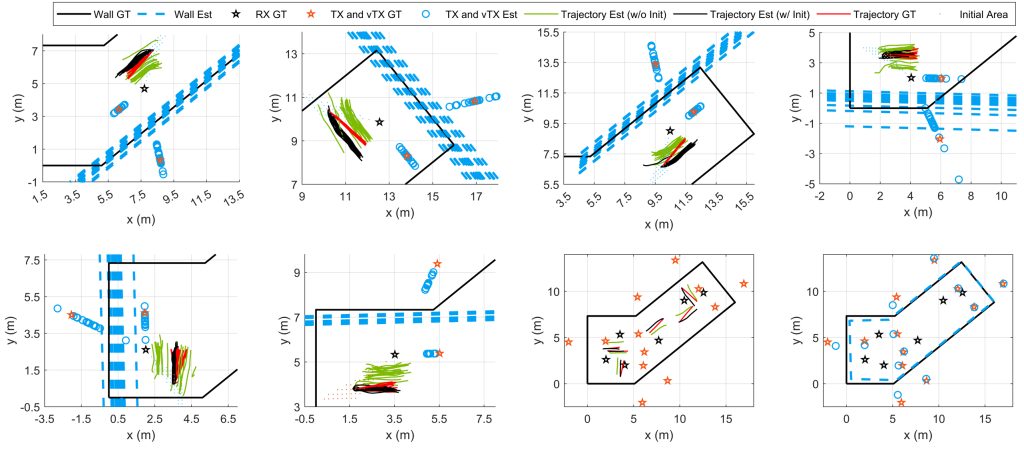
The target trajectory is estimated by jointly exploiting two signal paths: one line-of-sight (LoS) path and one wall-reflected non-line-of-sight (NLoS) path. Each path provides a distinct Doppler measurement corresponding to a different geometric line, and the combination of these two Doppler constraints enables two-dimensional motion estimation of the passive target. Meanwhile, the wall-reflected path is modeled as a virtual receiver, whose location can be inferred from the observed reflections, allowing the wall position and environmental layout to be reconstructed without dedicated sensing hardware.